在java线程中,每个线程都有一个ThreadLocalMap实例变量(如果不使用ThreadLocal,不会创建这个Map,一个线程第一次访问某个ThreadLocal变量时,才会创建)。该Map是使用线性探测的方式解决hash冲突的问题,如果没有找到空闲的slot,就不断往后尝试,直到找到一个空闲的位置,插入entry,这种方式在经常遇到hash冲突时,影响效率。

FastThreadLocal直接使用数组避免了hash冲突的发生,具体做法是:每一个FastThreadLocal实例创建时,分配一个下标index;分配index使用AtomicInteger实现,每个FastThreadLocal都能获取到一个不重复的下标。当调用ftl.get()方法获取值时,直接从数组获取返回,如return array[index],如下图:
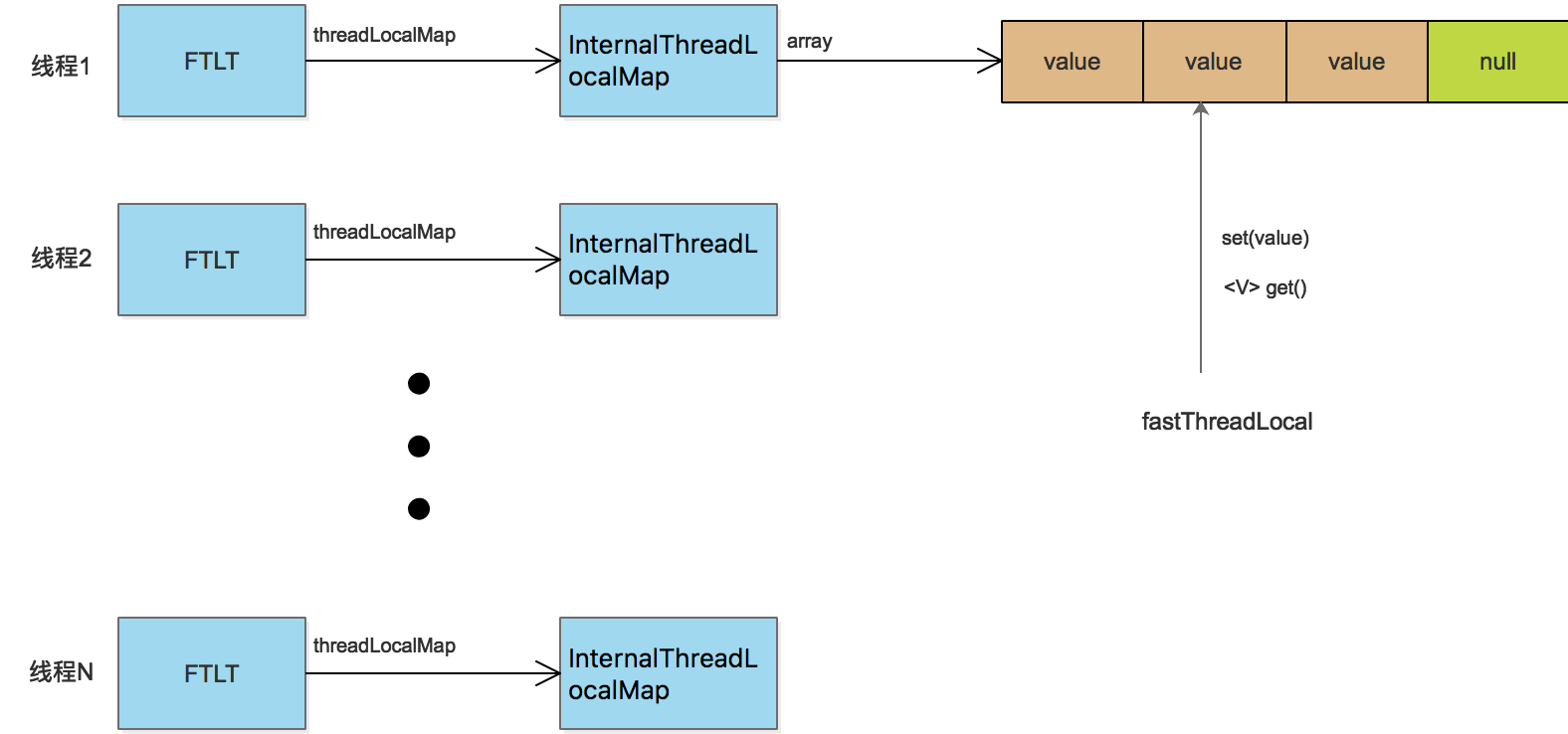
Netty 为 FastThreadLocal 量身打造了 FastThreadLocalThread 和 InternalThreadLocalMap 两个重要的类。下面我们看下这两个类是如何实现的。
FastThreadLocalThread 是对 Thread 类的一层包装,每个线程对应一个 InternalThreadLocalMap 实例。只有 FastThreadLocal 和 FastThreadLocalThread 组合使用时,才能发挥 FastThreadLocal 的性能优势。首先看下 FastThreadLocalThread 的源码定义:
public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {
// This will be set to true if we have a chance to wrap the Runnable.
private final boolean cleanupFastThreadLocals;
private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;
...
}
可以看出 FastThreadLocalThread 主要扩展了 InternalThreadLocalMap 字段,FastThreadLocalThread 主要使用 InternalThreadLocalMap 存储数据,而不再是使用 Thread 中的 ThreadLocalMap
接下来看下 InternalThreadLocalMap 的内部构造。
public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(InternalThreadLocalMap.class);
private static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =
new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
private static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
/** Used by {@link FastThreadLocal} */
private Object[] indexedVariables;
/**
* 用于标识FastThreadLocal变量是否注册了cleaner
* BitSet简要原理:
* BitSet默认底层数据结构是一个long[]数组,开始时长度为1,即只有long[0],而一个long有64bit。
* 当BitSet.set(1)的时候,表示将long[0]的第二位设置为true,即0000 0000 ... 0010(64bit),则long[0]==2
* 当BitSet.get(1)的时候,第二位为1,则表示true;如果是0,则表示false
* 当BitSet.set(64)的时候,表示设置第65位,此时long[0]已经不够用了,扩容处long[1]来,进行存储
*
* 存储类似 {index:boolean} 键值对,用于防止一个FastThreadLocal多次启动清理线程
* 将index位置的bit设为true,表示该InternalThreadLocalMap中对该FastThreadLocal已经启动了清理线程
*/
private BitSet cleanerFlags;
}
从 InternalThreadLocalMap 内部实现来看,与 ThreadLocalMap 一样都是采用数组的存储方式。但是 InternalThreadLocalMap 并没有使用线性探测法来解决 Hash 冲突,而是在 FastThreadLocal 初始化的时候分配一个数组索引 index,index 的值采用原子类 AtomicInteger 保证顺序递增,通过调用 InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex() 方法获得。然后在读写数据的时候通过数组下标 index 直接定位到 FastThreadLocal 的位置,时间复杂度为 O(1)。如果数组下标递增到非常大,那么数组也会比较大,所以 FastThreadLocal 是通过空间换时间的思想提升读写性能。
private final int index;
public FastThreadLocal() {
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();的实现
private static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
每个FastThreadLocal实例以步长为1的递增序列,获取index值,这保证了InternalThreadLocalMap中数组的长度不会突增。
下面我们来看一下FastThreadLocal的get方法
public final V get() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
// 如果获取到的值不是UNSET,那么是个有效的值,直接返回。如果是UNSET,则初始化。
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
return initialize(threadLocalMap);
}
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
// 当前线程是否为 FastThreadLocalThread 类型
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
// 获取 FastThreadLocalThread 的 threadLocalMap 属性
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
private static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =
new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
// 从 JDK 原生 ThreadLocal 中获取 InternalThreadLocalMap
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
如果当前线程是 FastThreadLocalThread 类型,那么直接通过 fastGet() 方法获取 FastThreadLocalThread 的 threadLocalMap 属性即可。如果此时 InternalThreadLocalMap 不存在,直接创建一个返回。关于 InternalThreadLocalMap 的初始化在上文中已经介绍过,它会初始化一个长度为 32 的 Object 数组,数组中填充着 32 个缺省对象 UNSET 的引用。
接下来看一下初始化方法initialize
private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
V v = null;
try {
// 获取初始值
v = initialValue();
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
// 保存到数组中,如果长度不够扩容
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, v);
// 将 FastThreadLocal 对象保存到待清理的 Set 中
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
return v;
}
private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {
// 获取数组下标为 0 的元素
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;
if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {
// 创建 FastThreadLocal 类型的 Set 集合
variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());
// 将 Set 集合填充到数组下标 0 的位置
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);
} else {
// 如果不是 UNSET,Set 集合已存在,直接强转获得 Set 集合
variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;
}
// 将 FastThreadLocal 添加到 Set 集合中
variablesToRemove.add(variable);
}
variablesToRemoveIndex 是采用 static final 修饰的变量,在 FastThreadLocal 初始化时 variablesToRemoveIndex 被赋值为 0。InternalThreadLocalMap 首先会找到数组下标为 0 的元素,如果该元素是缺省对象 UNSET 或者不存在,那么会创建一个 FastThreadLocal 类型的 Set 集合,然后把 Set 集合填充到数组下标 0 的位置。如果数组第一个元素不是缺省对象 UNSET,说明 Set 集合已经被填充,直接强转获得 Set 集合即可。这就解释了 InternalThreadLocalMap 的 value 数据为什么是从下标为 1 的位置开始存储了,因为 0 的位置已经被 Set 集合占用了。
为什么 InternalThreadLocalMap 要在数组下标为 0 的位置存放一个 FastThreadLocal 类型的 Set 集合呢?这时候我们回过头看下 remove() 方法。
public final void remove() {
remove(InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet());
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
return;
}
// 删除数组下标 index 位置对应的 value
Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);
// 从数组下标 0 的位置取出 Set 集合,并删除当前 FastThreadLocal
removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
try {
// 空方法,用户可以继承实现
onRemoval((V) v);
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
}
}
在执行 remove 操作之前,会调用 InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet() 获取当前 InternalThreadLocalMap。找到 InternalThreadLocalMap 之后,InternalThreadLocalMap 会从数组中定位到下标 index 位置的元素,并将 index 位置的元素覆盖为缺省对象 UNSET。接下来就需要清理当前的 FastThreadLocal 对象,此时 Set 集合就派上了用场,InternalThreadLocalMap 会取出数组下标 0 位置的 Set 集合,然后删除当前 FastThreadLocal。
set方法
public final void set(V value) {
// 1. value 是否为缺省值
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
// 2. 获取当前线程的 InternalThreadLocalMap
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
// 3. 将 InternalThreadLocalMap 中数据替换为新的 value
setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);
} else {
remove();
}
}
FastThreadLocal.set() 方法虽然入口只有几行代码,但是内部逻辑是相当复杂的。我们首先还是抓住代码主干,一步步进行拆解分析。set() 的过程主要分为三步:
-
判断 value 是否为缺省值,如果等于缺省值,那么直接调用 remove() 方法。这里我们还不知道缺省值和 remove() 之间的联系是什么,我们暂且把 remove() 放在最后分析。
-
如果 value 不等于缺省值,接下来会获取当前线程的 InternalThreadLocalMap。
-
然后将 InternalThreadLocalMap 中对应数据替换为新的 value。
