1. 接受请求
我们已经知道,ServerBootstrap会不停轮询NIO事件
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
// 这个Channel是NioServerSocketChannel
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
// 处理读请求和连接事件
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
}
进入NioMessageUnsafe#read方法可以发现最终调用了NioServerSocketChannel#doReadMessages用来初始化客户端的Channel
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
// 获取JDK的Channel
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
// 封装成NioSocketChannel
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
return 0;
}
跟踪NioSocketChannel的构造方法,发现它和NioServerSocketChannel一样,最终通过AbstractChannel初始化了pipeline。
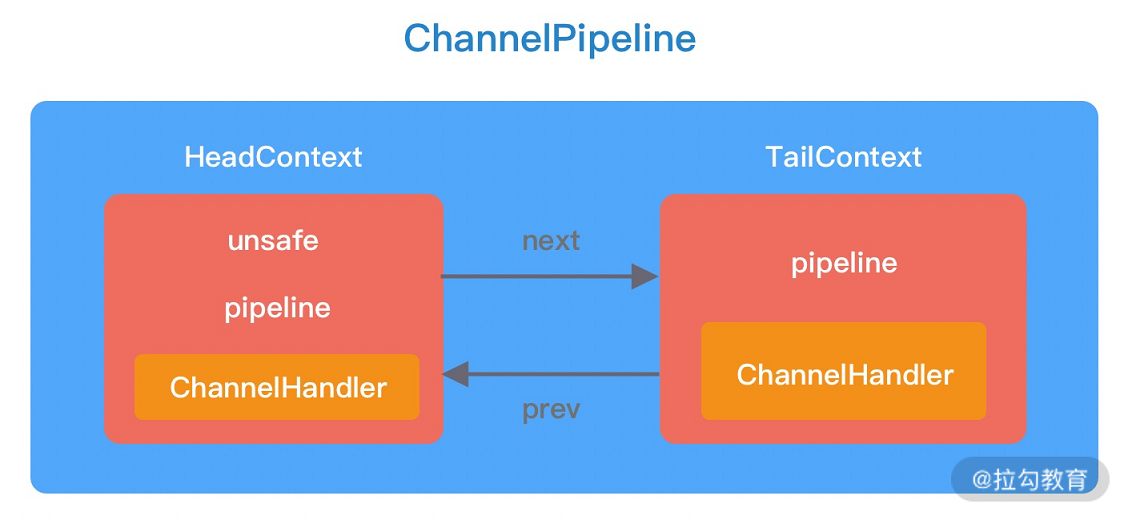
pipeline初始化了两个节点head、tail
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
之后会触发fireChannelRead,fireChannelReadComplete事件,msg都是NioSocketChannel
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
我们Server绑定Channel的时候注册了一个ServerBootstrapAcceptor的handler,fireChannelRead会触发ServerBootstrapAcceptor#channelRead,将我们自定义的childHandler绑定到pipeline中
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
// 绑定pipeline
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
setAttributes(child, childAttrs);
try {
// 通过workerReactor执行注册
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
和服务端Channel注册的过程基本相同。register方法会通过handlerAdded事件执行childHandler的initChannel来添加客户端的Handler。同时将childHandler从pipeline中删除。
2. 事件传播
我们再来看一下pipeline如何传播事件
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg) {
// 通过findContextInbound查询实现了channelRead的handler,如何通过invokeChannelRead执行
invokeChannelRead(findContextInbound(MASK_CHANNEL_READ), msg);
return this;
}
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound(int mask) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
EventExecutor currentExecutor = executor();
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (skipContext(ctx, currentExecutor, mask, MASK_ONLY_INBOUND));
return ctx;
}
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
一次fireChannelRead只会执行一个handler,如果需要传播事件,需要手动触发ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
接下来,我们看一下findContextInbound中用于判断handler是否需要执行channelRead方法的实现skipContext,可以看到它是通过一个executionMask属性来进行判断。跟踪源码可以发现executionMask是添加handler的时候就通过mask方法计算好的
AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor,
String name, Class<? extends ChannelHandler> handlerClass) {
this.name = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(name, "name");
this.pipeline = pipeline;
this.executor = executor;
this.executionMask = mask(handlerClass);
// Its ordered if its driven by the EventLoop or the given Executor is an instanceof OrderedEventExecutor.
ordered = executor == null || executor instanceof OrderedEventExecutor;
}
继续跟踪进入到mask0方法可以发现,Netty将所有的实践都定义了一个值,然后通过@Skip 注解排除 Handler 不感兴趣的事件呢?Handler 对应事件的方法上如果有 @Skip 注解,Netty 认为该事件是需要排除的。具体可以查看ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的实现
