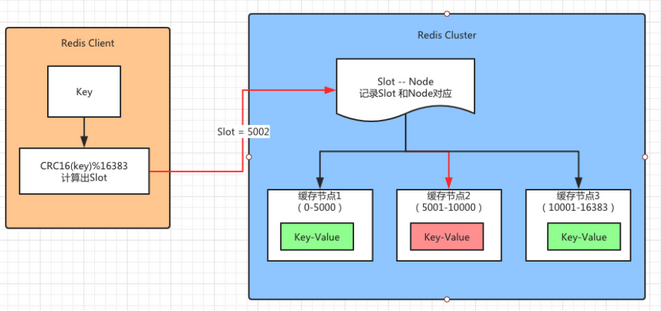
对于客户端请求的key,根据公式HASH_SLOT=CRC16(key) mod 16384,计算出映射到哪个分片上,然后Redis会去相应的节点进行操作!
CRC16算法产生的hash值有16bit,该算法可以产生2^16-=65536个值。换句话说,值是分布在0~65535之间。那作者在做mod运算的时候,为什么不mod65536,而选择mod16384?
https://github.com/antirez/redis/issues/2576The reason is:
- Normal heartbeat packets carry the full configuration of a node, that can be replaced in an idempotent way with the old in order to update an old config. This means they contain the slots configuration for a node, in raw form, that uses 2k of space with16k slots, but would use a prohibitive 8k of space using 65k slots.
- At the same time it is unlikely that Redis Cluster would scale to more than 1000 mater nodes because of other design tradeoffs.
So 16k was in the right range to ensure enough slots per master with a max of 1000 maters, but a small enough number to propagate the slot configuration as a raw bitmap easily. Note that in small clusters the bitmap would be hard to compress because when N is small the bitmap would have slots/N bits set that is a large percentage of bits set.
集群两个节点之间会定期发送ping/pong消息,交换数据信息,
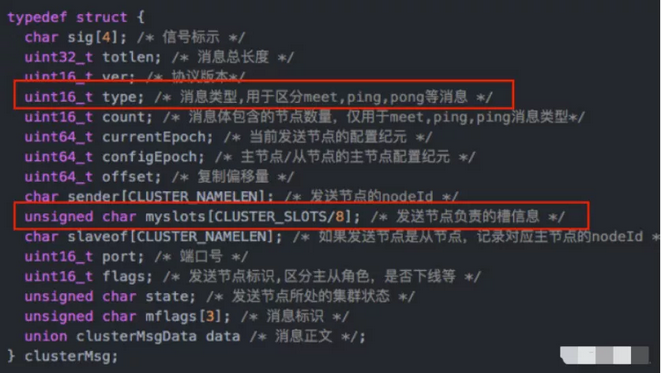
注意看红框的内容,type表示消息类型。 另外,消息头里面有个myslots的char数组,长度为16383/8,这其实是一个bitmap,每一个位代表一个槽,如果该位为1,表示这个槽是属于这个节点的。
在消息头中,最占空间的是myslots[CLUSTER_SLOTS/8]。这块的大小是:16384÷8÷1024=2kb
那在消息体中,会携带一定数量的其他节点信息用于交换。那这个其他节点的信息,约为集群总节点数量的1/10,至少携带3个节点的信息。
这里的重点是:节点数量越多,消息体内容越大。
消息体大小是10个节点的状态信息约1kb。
*那定期的频率是什么样的?
redis集群内节点,每秒都在发ping消息。规律如下
- (1)每秒会随机选取5个节点,找出最久没有通信的节点发送ping消息
- (2)每100毫秒(1秒10次)都会扫描本地节点列表,如果发现节点最近一次接受pong消息的时间大于cluster-node-timeout/2 则立刻发送ping消息
因此,每秒单节点发出ping消息数量为1+10*num(node.pong_received>cluster_node_timeout/2)
那大致带宽损耗如下所示,图片来自《Redis开发与运维》

(1)如果槽位为65536,发送心跳信息的消息头达8k,发送的心跳包过于庞大。
如上所述,在消息头中,最占空间的是myslots[CLUSTER_SLOTS/8]。当槽位为65536时,这块的大小是:65536÷8÷1024=8kb
因为每秒钟,redis节点需要发送一定数量的ping消息作为心跳包,如果槽位为65536,这个ping消息的消息头太大了,浪费带宽。
(2)redis的集群主节点数量基本不可能超过1000个。
如上所述,集群节点越多,心跳包的消息体内携带的数据越多。如果节点过1000个,也会导致网络拥堵。因此redis作者,不建议redis cluster节点数量超过1000个。
那么,对于节点数在1000以内的redis cluster集群,16384个槽位够用了。没有必要拓展到65536个。
(3)槽位越小,节点少的情况下,压缩率高
Redis主节点的配置信息中,它所负责的哈希槽是通过一张bitmap的形式来保存的,在传输过程中,会对bitmap进行压缩,但是如果bitmap的填充率slots / N很高的话(N表示节点数),bitmap的压缩率就很低。
如果节点数很少,而哈希槽数量很多的话,bitmap的压缩率就很低。
参考资料
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vJdy3f_Aoc5mZsbWAR1uRw
